Get ready to dive into the world of retirement age statistics with a fresh perspective, where we unravel the trends and factors shaping this crucial aspect of global economics and policy-making.
From demographic shifts to cultural influences, we explore the intricate web of factors that determine when individuals choose to retire.
Introduction to Retirement Age Statistics
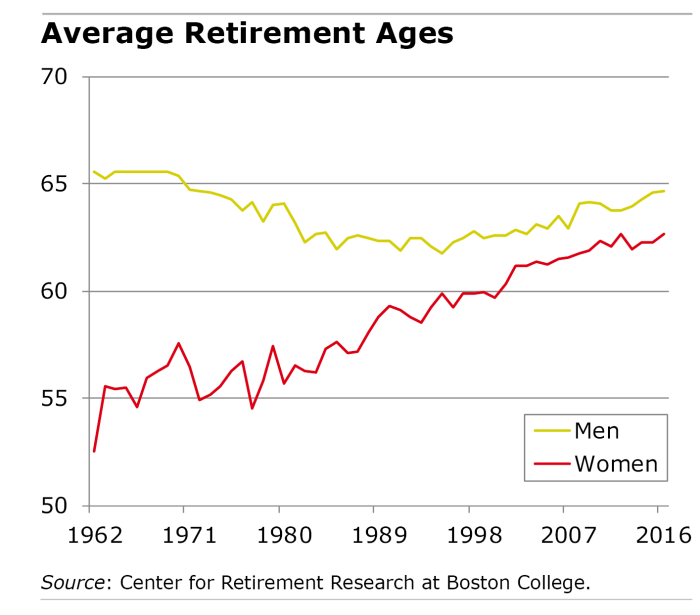
Retirement age, the age at which individuals typically stop working and begin to rely on their savings, pension, or social security, varies significantly across different countries. Understanding retirement age statistics is crucial for policymakers and economists to make informed decisions regarding social security programs, labor force participation, and economic planning.
Evolution of Retirement Age Trends
Over the years, retirement age trends have shifted due to various factors such as changes in life expectancy, economic conditions, and government policies. Let’s take a closer look at how retirement age statistics have evolved:
- In the early 20th century, retirement age was often around 65 years old, coinciding with the establishment of social security programs in many countries.
- As life expectancy has increased, some countries have raised the official retirement age to address concerns about the sustainability of pension systems.
- On the other hand, there has been a growing trend towards flexible retirement options, allowing individuals to gradually transition out of the workforce instead of abruptly stopping at a certain age.
- Recent discussions also focus on the challenges of an aging workforce and the need to encourage older workers to stay in the labor market longer to support economic growth.
Factors Influencing Retirement Age
Deciding when to retire is influenced by a variety of factors, including demographic, economic, cultural, and social considerations. Let’s delve into the key influences that impact retirement age decisions.
Demographic Factors
Demographic factors such as life expectancy, health status, and family structure play a significant role in determining retirement age. For instance, individuals in countries with higher life expectancies tend to retire later, while those with health issues may retire earlier to focus on their well-being.
Economic Conditions
Economic conditions in different regions can greatly affect retirement age decisions. In countries with stable economies and robust pension systems, individuals may feel more financially secure to retire at an older age. On the contrary, in regions with economic instability or limited retirement benefits, people may be forced to retire earlier or work longer to make ends meet.
Cultural and Social Norms
Cultural and social norms also influence the choice of retirement age. In some cultures, there is a strong emphasis on working hard and providing for the family, leading individuals to delay retirement. Conversely, societies that value leisure and relaxation may encourage earlier retirement. Moreover, the stigma or perception of aging in the workforce can impact when individuals decide to retire.
Global Comparison of Retirement Age
When it comes to retirement age, there are significant differences across different continents. Developed countries tend to have higher retirement ages compared to developing nations. This is due to factors such as life expectancy, economic stability, and social security systems.
Retirement Age in Europe
- In countries like Germany and France, the retirement age is around 65 years old.
- Some European countries have implemented policies to gradually increase the retirement age to cope with an aging population.
- Generous pension systems in Europe allow for early retirement in some cases.
Retirement Age in Asia
- Asian countries like Japan and South Korea have retirement ages set around 60-65 years old.
- In countries such as China and India, the retirement age varies depending on the sector and occupation.
- Asian nations are facing challenges in increasing retirement ages due to cultural norms and workforce dynamics.
Retirement Age in Africa
- Many African countries have retirement ages set around 60 years old.
- Issues such as lack of formal social security systems contribute to early retirements in some African nations.
- Some African countries are working towards increasing retirement ages to ensure financial sustainability.
Retirement Age in the Americas
- Countries in North America like the United States have retirement ages around 65-67 years old.
- In Latin America, retirement ages vary significantly from country to country.
- The debate over raising retirement ages in the Americas continues due to changing demographics and economic factors.
Retirement Age Trends in Specific Countries
In this section, we will explore the retirement age trends in various countries around the world, including the United States, Europe, Asia, and other regions. We will provide statistics on the average retirement age in key countries and identify any recent changes or reforms in retirement age policies.
United States
The average retirement age in the United States is around 66 years old. However, with the shift towards a more flexible and personalized approach to retirement, many Americans are choosing to work beyond the traditional retirement age. Recent reforms have focused on increasing the full retirement age for Social Security benefits, encouraging individuals to work longer.
Europe
In Europe, retirement age varies significantly from country to country. For example, countries like France and Greece have historically had lower retirement ages, while countries like Germany and the United Kingdom have been increasing the retirement age in response to demographic changes and economic pressures. The average retirement age in Europe is around 65 years old.
Asia
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea are facing challenges related to an aging population and shrinking workforce. As a result, these countries have been gradually increasing the retirement age to ensure the sustainability of their pension systems. The average retirement age in Asia is also around 65 years old.
Other Regions
Other regions, such as Australia and Canada, have also been adjusting their retirement age policies to address similar demographic and economic challenges. These countries are exploring ways to encourage older individuals to remain in the workforce longer while also providing adequate support for those who choose to retire early. The average retirement age in these regions hovers around 65-67 years old.
Gender Disparities in Retirement Age
Gender plays a significant role in retirement age decisions, with disparities between male and female retirement ages prevalent worldwide. These differences are influenced by various factors such as societal norms, career choices, and caregiving responsibilities.
Factors Influencing Gender Disparities in Retirement Age
- Historical gender roles: Traditional roles assigned to men and women have influenced retirement age norms, with men often encouraged to work longer than women.
- Pay gap: The gender pay gap may result in women needing to work longer to achieve financial security in retirement, leading to later retirement ages.
- Caregiving responsibilities: Women are more likely to take on caregiving roles for children or elderly parents, impacting their ability to retire early.
Impact of Gender Equality Initiatives on Retirement Age
- Gender equality initiatives aimed at closing the pay gap and promoting equal opportunities in the workforce can lead to more balanced retirement ages between men and women.
- Policies supporting work-life balance and flexible work arrangements can help women manage caregiving responsibilities while maintaining their careers, potentially leading to earlier retirement ages.
- Increased representation of women in leadership positions can challenge traditional gender norms and empower women to make independent decisions about their retirement age.
Retirement Age and Workforce Dynamics
In today’s rapidly changing work landscape, the relationship between retirement age and workforce dynamics plays a crucial role in shaping labor policies and economic strategies.
Impact on Workforce Participation Rates
- As retirement age increases, workforce participation rates tend to rise as well, leading to a larger pool of experienced workers contributing to the economy.
- This trend can affect the overall productivity of a country and potentially offset the challenges posed by an aging population.
- Employers may also benefit from retaining experienced employees for longer periods, reducing the need for constant recruitment and training.
Implications of an Aging Workforce
- An aging workforce presents challenges in terms of adapting workplace environments to accommodate older employees and their specific needs.
- Companies may need to invest in training programs to update skills and knowledge of older workers, ensuring they remain competitive in the job market.
- Retirement age policies may need to be flexible to allow individuals to transition out of the workforce gradually, balancing the needs of older workers with those of younger generations entering the workforce.
Impact on Retirement Savings and Pension Systems
- Increasing retirement age can have a positive effect on retirement savings, allowing individuals to accumulate more funds for their post-work years.
- However, it also puts pressure on pension systems to adapt to longer life expectancies and increased demand for benefits over an extended period.
- Policy makers need to consider the sustainability of pension schemes and explore innovative solutions to ensure financial security for retirees in the face of a shifting retirement age landscape.
