Product Pricing Strategies takes center stage, inviting readers into a world where setting prices is an art form. From cost-plus to skimming, get ready to dive into the dynamic world of pricing strategies.
In this exploration, we’ll uncover the secrets behind successful pricing decisions and the factors that drive consumer behavior.
Overview of Product Pricing Strategies
Product pricing strategies are essential tactics used by businesses to determine the optimal price for their products or services. This decision is crucial as it directly impacts consumer behavior and purchasing decisions. By strategically setting prices, businesses can attract customers, increase sales, and ultimately maximize profits. It is important for companies to align their pricing strategies with their business goals and target market in order to remain competitive and achieve long-term success.
Significance of Pricing in Business
- Price is a key factor that influences consumer behavior and purchasing decisions.
- Proper pricing strategies can help businesses differentiate themselves from competitors.
- Effective pricing can lead to increased market share and revenue growth.
Role of Pricing in Influencing Consumer Behavior
- Price can signal the quality and value of a product to consumers.
- Discounts and promotions can create a sense of urgency and drive purchase decisions.
- Pricing transparency can build trust with customers and encourage repeat purchases.
Importance of Aligning Pricing Strategies, Product Pricing Strategies
- Understanding the target market’s price sensitivity is crucial for setting the right prices.
- Consistent pricing helps establish brand identity and loyalty among customers.
- Regularly evaluating and adjusting pricing strategies ensures competitiveness in the market.
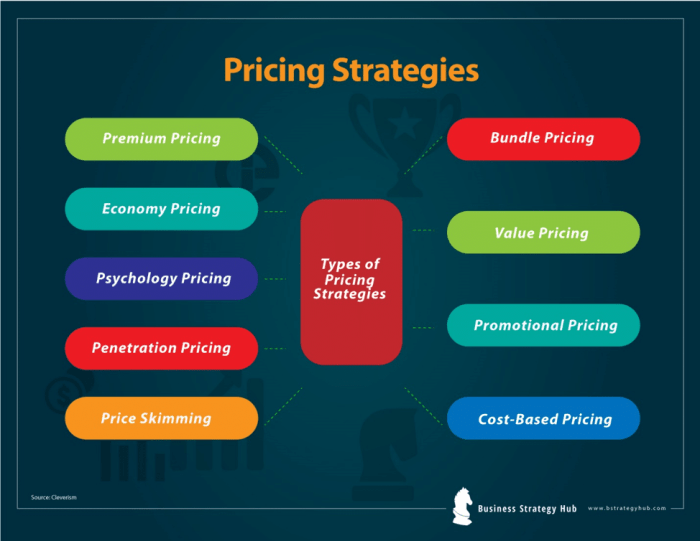
Common Pricing Strategies
In the world of business, pricing strategies play a crucial role in determining the success of a product or service. Let’s explore some popular pricing strategies and how companies utilize them to their advantage.
Cost-Plus Pricing
Cost-plus pricing involves calculating the total cost of production and adding a markup to determine the final price. This strategy ensures that the company covers all costs and generates a profit.
- Example: Walmart uses cost-plus pricing for its private label products, setting prices based on production costs and desired profit margins.
Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing focuses on the perceived value of a product or service to customers. Companies set prices based on what customers are willing to pay, rather than just production costs.
- Example: Apple is known for implementing value-based pricing for its premium products like the iPhone, pricing them higher due to the perceived value and quality.
Penetration Pricing
Penetration pricing involves setting a low initial price to attract customers and gain market share quickly. Once a customer base is established, prices may be increased.
- Example: Amazon used penetration pricing when launching its Kindle e-reader, offering it at a low price to encourage adoption and later increasing prices.
Skimming Pricing
Skimming pricing involves setting a high initial price to target early adopters and customers willing to pay a premium. Over time, prices are lowered to attract more price-sensitive customers.
- Example: Sony used skimming pricing for the PlayStation 5 console, launching it at a high price to target hardcore gamers before gradually reducing prices for a wider audience.
Factors Influencing Pricing Decisions
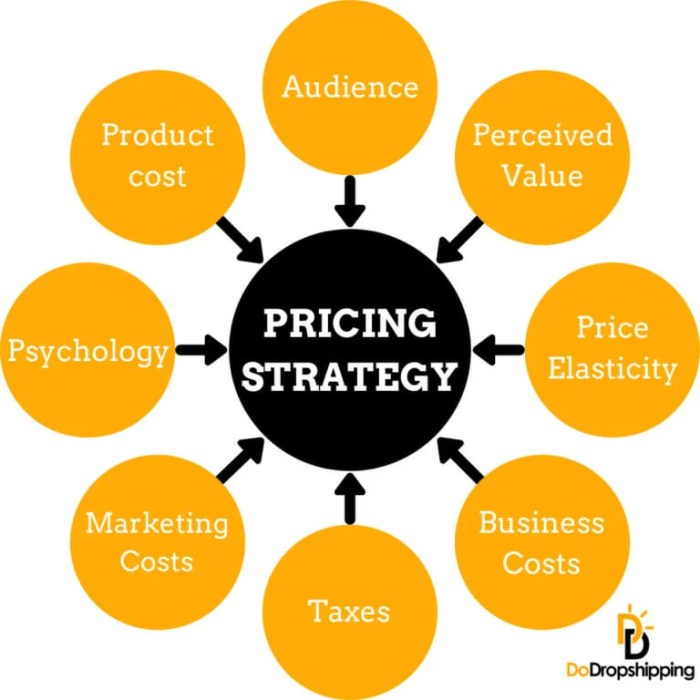
In the world of business, setting the right price for a product or service is crucial for success. Several key factors influence pricing decisions, shaping the strategy that companies choose to adopt.
Market demand plays a significant role in pricing decisions. Understanding the level of demand for a product or service helps businesses determine the optimal price point that will attract customers while maximizing revenue. High demand typically allows for higher prices, while low demand may require competitive pricing strategies to stimulate sales.
Competition in the market also heavily influences pricing decisions. Businesses need to consider the prices set by their competitors and position their products accordingly. Price wars, where companies continually lower prices to gain a competitive edge, can have a significant impact on pricing strategies.
Production costs are another essential factor to consider when setting prices. Companies must ensure that the price covers the cost of production while still providing a reasonable profit margin. High production costs may necessitate higher prices, while efficient production processes can allow for more competitive pricing.
Perceived value is a crucial factor that affects pricing decisions. Customers are willing to pay more for products they perceive as having higher value. Companies must effectively communicate the value of their products to justify the price to consumers.
Pricing Elasticity and its Impact
Pricing elasticity refers to how sensitive consumers are to price changes. Understanding pricing elasticity is essential for businesses to determine the optimal pricing strategy.
- Price Elasticity of Demand: This concept measures the responsiveness of demand to a change in price. Products with elastic demand are highly sensitive to price changes, while products with inelastic demand are less affected by price fluctuations.
- Impact on Pricing Strategies: Businesses must consider pricing elasticity when setting prices. For products with elastic demand, lowering prices may increase sales volume but reduce revenue per unit. In contrast, products with inelastic demand may allow for price increases without significant loss in sales volume.
- Adjusting Pricing Strategies: By analyzing pricing elasticity, companies can make informed decisions about price adjustments. They can experiment with different price points to find the optimal balance between sales volume and revenue.
Dynamic Pricing and Personalized Pricing
Dynamic pricing is a strategy where prices are adjusted in real-time based on various factors such as demand, competitor prices, and customer behavior. This strategy is commonly used in e-commerce and retail industries to optimize revenue and profit margins.
Dynamic Pricing in E-commerce and Retail
Dynamic pricing algorithms analyze market conditions to set prices that are most likely to maximize profit. This can lead to fluctuating prices for products based on factors like time of day, seasonality, and even individual customer browsing history. For example, airlines often use dynamic pricing to adjust ticket prices based on demand and seat availability.
Personalized Pricing Strategies
- Personalized pricing involves tailoring prices to individual customers based on their purchase history, preferences, and willingness to pay. This can be achieved through loyalty programs, targeted discounts, or personalized promotions.
- By offering personalized pricing, businesses can increase customer loyalty and satisfaction, ultimately driving sales and revenue. For example, online retailers may offer exclusive discounts to customers who have previously abandoned their shopping carts.
Ethical Implications of Dynamic and Personalized Pricing
While dynamic pricing and personalized pricing can be beneficial for businesses, there are ethical concerns regarding fairness and transparency. Customers may feel exploited if they perceive prices to be unfairly inflated based on their browsing history or demographic information. It is important for businesses to be transparent about their pricing strategies and ensure that customers feel valued and respected.
