Get ready to dive into the world of investment portfolio management, where strategic decisions and financial prowess intersect. This guide will walk you through the ins and outs of effectively managing your investments, ensuring maximum returns and minimal risks.
Introduction to Investment Portfolio Management
Investment portfolio management refers to the process of overseeing a person’s or entity’s investments to achieve specific financial goals. This involves making decisions about what assets to invest in, how much to allocate to each asset, and when to buy or sell these assets.
Importance of Managing an Investment Portfolio Effectively
Effective management of an investment portfolio is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it helps individuals or organizations in achieving their financial objectives, whether it be saving for retirement, funding a child’s education, or generating passive income. By actively managing their investments, individuals can maximize returns and minimize risks, ultimately growing their wealth over time.
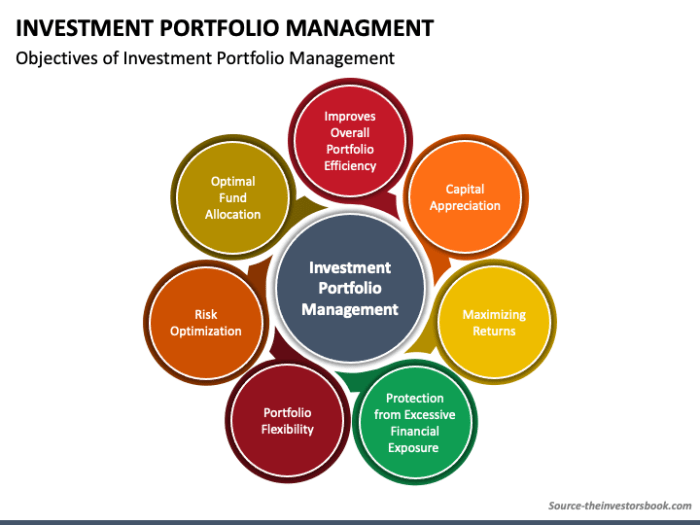
Key Objectives of Investment Portfolio Management
- Maximizing returns: One of the primary objectives of investment portfolio management is to generate the highest possible returns given the level of risk tolerance of the investor. This involves selecting the right mix of assets that have the potential for growth.
- Risk management: Another key objective is to effectively manage risk by diversifying the investment portfolio. Diversification helps spread risk across different asset classes, reducing the impact of any single investment performing poorly.
- Liquidity management: Investment portfolio management also focuses on maintaining liquidity to meet short-term financial needs. By balancing liquid assets with long-term investments, investors can access funds when needed without having to sell off long-term holdings at a loss.
- Adapting to market conditions: The ability to adjust the investment portfolio based on changing market conditions is essential for long-term success. Monitoring economic trends, geopolitical events, and industry developments allows investors to make informed decisions that align with their financial goals.
Types of Investment Portfolios
Investment portfolios can be categorized into different types based on their objectives and composition. Each type has unique characteristics that cater to specific investor needs and risk preferences.
Growth Portfolio
A growth portfolio focuses on capital appreciation by investing in high-growth companies or sectors. These portfolios typically contain stocks of companies with strong growth potential. The key characteristic of a growth portfolio is that it aims for long-term capital growth rather than immediate income generation. While these portfolios can offer high returns, they also come with higher volatility and risk.
Income Portfolio
An income portfolio is designed to provide a steady stream of income for investors. This type of portfolio typically includes bonds, dividend-paying stocks, and other income-generating assets. The primary goal of an income portfolio is to generate regular income for investors, making it suitable for retirees or those looking for passive income. Income portfolios generally have lower volatility compared to growth portfolios but may offer lower returns.
Balanced Portfolio
A balanced portfolio, as the name suggests, aims to strike a balance between growth and income. These portfolios typically contain a mix of growth-oriented assets like stocks and income-generating assets like bonds. The objective of a balanced portfolio is to provide both capital appreciation and income while managing risk. Balanced portfolios are suitable for investors looking for a moderate level of risk and return.
Comparing the risk-return profiles of these different types of investment portfolios, growth portfolios tend to offer the highest potential returns but also come with the highest level of risk due to their focus on growth stocks. Income portfolios, on the other hand, offer more stability and lower risk but may have lower returns. Balanced portfolios aim to provide a middle ground, offering a mix of growth and income assets to balance risk and return.
Strategies for Investment Portfolio Management
Investment portfolio management involves various strategies to maximize returns and minimize risks. Let’s delve into some key strategies used by investors.
Modern Portfolio Theory
Modern Portfolio Theory, developed by Harry Markowitz, is a framework that emphasizes diversification to optimize returns for a given level of risk. It suggests that by combining assets with low correlation, investors can achieve a more efficient portfolio. The theory focuses on the trade-off between risk and return, helping investors make informed decisions about asset allocation.
Diversification and Risk Management
Diversification is a key strategy in investment portfolio management that involves spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions. By diversifying, investors can reduce the impact of any single asset’s performance on the overall portfolio. This helps to minimize risk and volatility, as losses in one asset may be offset by gains in another.
Active vs. Passive Investment Strategies
Active investment strategies involve frequent buying and selling of assets in an attempt to outperform the market. This approach requires skill and market timing, but it also incurs higher fees and transaction costs. On the other hand, passive investment strategies aim to replicate the performance of a specific market index or benchmark. These strategies typically have lower fees and are more focused on long-term growth rather than short-term gains. The choice between active and passive strategies depends on an investor’s risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon.
Asset Allocation in Investment Portfolios
Asset allocation is a crucial aspect of portfolio management that involves distributing investments across different asset classes to achieve a balance between risk and return. By diversifying across various types of assets, investors can reduce the overall risk of their portfolios and optimize returns.
Significance of Asset Allocation
Asset allocation plays a key role in determining the overall performance of an investment portfolio. It helps investors spread their risk exposure and capitalize on different market conditions. By strategically allocating assets, investors can enhance their chances of achieving their financial goals while minimizing potential losses.
- Asset allocation allows investors to achieve a balance between risk and return.
- Diversification helps in reducing the overall risk of the portfolio.
- By spreading investments across different asset classes, investors can capture opportunities in various market conditions.
Factors Influencing Asset Allocation Decisions
Several factors influence asset allocation decisions, including an investor’s risk tolerance, investment goals, time horizon, and market conditions. It is essential to consider these factors when determining the optimal allocation of assets within a portfolio.
- Investor’s Risk Tolerance: Determines the level of risk an investor is comfortable with.
- Investment Goals: Goals such as capital preservation, income generation, or capital appreciation influence asset allocation.
- Time Horizon: Short-term or long-term investment horizon impacts asset allocation decisions.
- Market Conditions: Economic environment, interest rates, and market trends affect asset allocation strategies.
Examples of Asset Allocation Strategies
Asset allocation strategies can vary based on different investment goals and risk profiles. Here are some common examples of asset allocation strategies:
- Conservative Portfolio: Emphasizes capital preservation and income generation, with a higher allocation to fixed-income securities.
- Moderate Portfolio: Balances risk and return by diversifying across equities, bonds, and alternative investments.
- Aggressive Portfolio: Seeks high returns by allocating a significant portion to equities and other high-risk assets.
Performance Evaluation of Investment Portfolios
Investors and financial managers often assess the performance of investment portfolios to gauge their effectiveness in achieving financial goals and objectives.
Measurement of Investment Portfolio Performance
Investment portfolio performance is typically measured using various key metrics that provide insights into the portfolio’s profitability and risk levels. Some common metrics include:
- Return on Investment (ROI): Calculated as the percentage gain or loss on an investment relative to the initial investment amount.
- Sharpe Ratio: Measures the risk-adjusted return of a portfolio, taking into account the level of risk involved in generating returns.
- Alpha: Indicates the excess return of a portfolio compared to its benchmark index, reflecting the manager’s skill in generating returns.
Importance of Benchmarking in Portfolio Performance Assessment
Benchmarking plays a crucial role in evaluating the success of an investment portfolio by providing a reference point for comparison. By comparing portfolio performance against a relevant benchmark, investors can assess how well the portfolio has performed in relation to the market or industry standards. This helps in identifying whether the portfolio manager has added value through active management strategies or not.
