Investing for Beginners takes center stage, inviting you into a world of financial knowledge with an American high school hip flair. Get ready to dive into the basics of investing and start your journey to financial success.
From understanding different investment types to managing risks and building a diversified portfolio, this guide will equip you with the essential tools to kickstart your investment journey.
Understanding the Basics of Investing: Investing For Beginners

Investing is the process of putting money into financial assets with the expectation of generating profits or income over time. It involves taking calculated risks to grow your wealth and achieve financial goals.
Types of Investments
- Stocks: Ownership in a company, providing potential for capital appreciation and dividends.
- Bonds: Loans made to governments or corporations, offering fixed interest payments.
- Real Estate: Property ownership for rental income or capital appreciation.
Setting Investment Goals
Investment goals are essential to guide your decisions and measure success. Whether it’s saving for retirement, buying a house, or funding education, clear goals help you stay focused and motivated.
Short-term vs. Long-term Investing
- Short-term: Buying and selling assets within a short period, focusing on quick returns or market fluctuations.
- Long-term: Holding investments for an extended period, aiming for gradual growth and compounding returns over time.
Risk Management in Investing
When it comes to investing, risk is the possibility of losing money or not achieving the expected return on an investment. Understanding and managing risk is crucial for successful investing.
Diversification and its Importance
Diversification is a strategy where you spread your investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographic locations. This helps reduce the overall risk in your investment portfolio because if one investment performs poorly, others may perform well, balancing out your returns.
- Diversification is important because it helps minimize the impact of market volatility on your portfolio.
- By spreading your investments, you are not putting all your eggs in one basket, reducing the risk of losing a significant portion of your investment.
- It is essential to have a mix of investments with different risk levels to achieve a balanced portfolio.
Relationship between Risk and Return
The relationship between risk and return is often described as the higher the risk, the higher the potential return, and vice versa. Investors need to find a balance between risk and return that aligns with their investment goals and risk tolerance.
It is important to remember that higher returns usually come with higher risks, and vice versa.
Mitigating Risk through Asset Allocation, Investing for Beginners
Asset allocation is the strategy of dividing your investment portfolio among different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents. This helps reduce risk by spreading your investments across different categories that may react differently to market conditions.
- Allocate your assets based on your investment goals, time horizon, and risk tolerance.
- Regularly review and rebalance your portfolio to maintain your desired asset allocation mix.
- Consider investing in assets with low correlation to further diversify and reduce risk.
Investment Vehicles for Beginners
Investing in the stock market can be overwhelming for beginners, but understanding different investment vehicles can help you make informed decisions. Let’s take a look at individual stocks, mutual funds, and ETFs to see which one might be the right fit for you.
Individual Stocks
Individual stocks represent ownership in a specific company. Here are some pros and cons to consider:
- Pros:
- Potential for high returns if the stock performs well.
- You have control over which companies to invest in.
- Cons:
- Higher risk due to lack of diversification.
- Requires more time and research to pick winning stocks.
Mutual Funds
Mutual funds pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks and bonds. Here are the pros and cons:
- Pros:
- Instant diversification across various assets.
- Professional management by fund managers.
- Cons:
- Fees can be higher compared to individual stock investing.
- You have no control over specific investments within the fund.
ETFs
ETFs are similar to mutual funds but trade on stock exchanges like individual stocks. Here are the pros and cons:
- Pros:
- Low expense ratios compared to mutual funds.
- Can be bought and sold throughout the trading day.
- Cons:
- Brokerage commissions may apply for buying and selling.
- Some ETFs may have less liquidity than others.
Choosing the Right Investment Vehicle
When deciding on an investment vehicle, consider your risk tolerance and financial goals. If you prefer a hands-on approach and are willing to take on more risk, individual stocks could be a good fit. For those seeking diversification and professional management, mutual funds or ETFs might be more suitable. Remember to compare the fees associated with each option and choose based on what aligns with your investment strategy.
Building a Diversified Portfolio
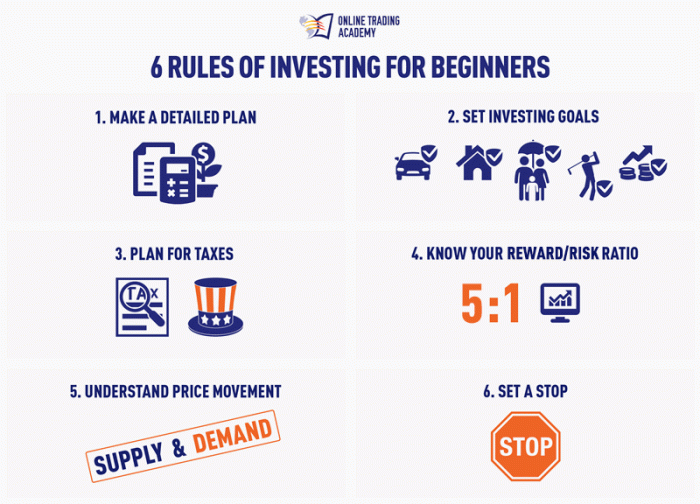
Diversification is a key strategy in investing that involves spreading your investments across different asset classes to reduce risk and increase the potential for returns. By diversifying your portfolio, you can protect yourself from the volatility of any single investment.
Importance of Diversification
Diversification helps in reducing the overall risk of your portfolio by not putting all your eggs in one basket. It ensures that a loss in one investment is not catastrophic to your entire portfolio.
Guidelines for Building a Diversified Portfolio
- Invest in a mix of asset classes such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities.
- Diversify within each asset class by investing in different industries or sectors.
- Consider incorporating international investments to further diversify geographically.
- Regularly rebalance your portfolio to maintain the desired asset allocation.
Role of Asset Allocation
Asset allocation refers to how you distribute your investments among different asset classes based on your risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon. It plays a crucial role in creating a balanced portfolio that aligns with your financial objectives.
Examples of Diversified Portfolios
| Risk Profile | Investment Allocation |
|---|---|
| Conservative | 60% bonds, 30% stocks, 10% cash |
| Moderate | 40% stocks, 40% bonds, 10% real estate, 10% commodities |
| Aggressive | 70% stocks, 20% real estate, 10% commodities |
