User Behavior Analytics is the key to unlocking the mysteries of cybersecurity, diving deep into the realm of insider threats and cutting-edge tools. Get ready for a wild ride through the world of digital behavior!
From rule-based to machine learning approaches, we explore the nuances of anomaly detection and the power of predictive analytics in deciphering user actions. Strap in for a thrilling journey into the heart of cybersecurity!
Overview of User Behavior Analytics
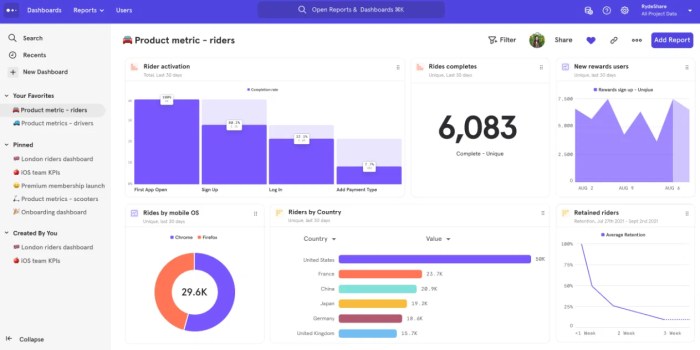
User Behavior Analytics (UBA) is a cybersecurity approach that focuses on monitoring and analyzing the behavior of users within an organization’s network. By tracking patterns and anomalies in user activity, UBA helps in identifying potential security threats, such as insider attacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access.
Importance of User Behavior Analytics in Cybersecurity
User behavior analytics plays a crucial role in cybersecurity by providing organizations with insights into normal user activities and deviations from the norm. This proactive approach enables early detection of suspicious behavior, reducing the risk of security incidents and minimizing the impact of potential threats.
- UBA helps in detecting insider threats by monitoring user actions, such as accessing sensitive data, unusual login times, or unauthorized file transfers.
- By analyzing user behavior in real-time, UBA can identify potential security risks before they escalate, allowing organizations to take immediate action to mitigate threats.
- UBA provides a holistic view of the organization’s security posture, enabling security teams to prioritize and respond to incidents effectively.
Key Components of User Behavior Analytics
User behavior analytics involves several key components that work together to provide comprehensive security insights:
- Data Collection: UBA tools gather data from various sources, such as logs, network traffic, and endpoint devices, to create a baseline of normal user behavior.
- Behavioral Analysis: UBA algorithms analyze user actions, interactions, and patterns to detect anomalies or deviations from the established baseline.
- Anomaly Detection: UBA systems use machine learning and AI to identify suspicious activities that may indicate a security threat, such as unauthorized access or data exfiltration.
- Alerting and Response: UBA tools generate alerts for security teams to investigate and respond to potential threats promptly, helping in preventing security incidents.
Examples of Tools for Implementing User Behavior Analytics
There are several UBA tools available in the market that organizations can leverage to enhance their cybersecurity posture:
Splunk User Behavior Analytics: A platform that uses machine learning to detect advanced threats and insider attacks by analyzing user behavior across the network.
Securonix: An advanced security analytics platform that provides real-time monitoring and detection of insider threats through behavior analytics and threat intelligence.
Exabeam: A user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) solution that helps organizations detect and respond to security incidents by analyzing user behavior and identifying abnormal activities.
Types of User Behavior Analytics
When it comes to analyzing user behavior, there are different approaches that can be taken to gain insights. Two main types of user behavior analytics are rule-based and machine learning-based techniques.
Distinguishing Rule-based and Machine Learning-based User Behavior Analytics
Rule-based user behavior analytics rely on predefined rules and thresholds to detect anomalies or patterns in user behavior. These rules are typically set by analysts based on their knowledge and experience. On the other hand, machine learning-based user behavior analytics use algorithms to analyze data and identify patterns without the need for explicit rules. Machine learning models can adapt and learn from new data, making them more flexible and scalable compared to rule-based approaches.
Anomaly Detection in User Behavior Analytics
Anomaly detection plays a crucial role in user behavior analytics by identifying unusual patterns or outliers in user activities. This helps organizations detect potential security threats, fraud, or abnormal behavior that may require further investigation. By leveraging anomaly detection techniques, such as clustering or statistical methods, organizations can proactively address suspicious activities and mitigate risks.
Comparing Supervised and Unsupervised Learning in User Behavior Analytics
Supervised learning in user behavior analytics involves training a model on labeled data to predict or classify user behavior based on predefined outcomes. This approach requires a significant amount of labeled data and is suitable for tasks like fraud detection or sentiment analysis. Unsupervised learning, on the other hand, does not require labeled data and focuses on identifying hidden patterns or clusters in user behavior. This approach is useful for exploring unknown insights or detecting anomalies in user activities.
Role of Predictive Analytics in Understanding User Behavior
Predictive analytics plays a vital role in understanding user behavior by forecasting future trends or outcomes based on historical data. By leveraging predictive models, organizations can anticipate user preferences, identify potential churn risks, or personalize user experiences. Predictive analytics enables organizations to make informed decisions and optimize their strategies to meet user needs effectively.
Implementing User Behavior Analytics
When it comes to setting up a user behavior analytics system, there are several key steps involved. First, you need to clearly define your goals and objectives for implementing the system. This will help guide the rest of the process and ensure that you are collecting the right data to meet your needs.
Data Collection and Aggregation
- Start by identifying the data sources that will be relevant to your analysis, such as website traffic, app usage, or customer interactions.
- Implement tools and technologies to collect data from these sources, ensuring that the data is accurate and consistent.
- Aggregate the collected data into a centralized database or data warehouse for easier analysis and reporting.
- Regularly review and clean the data to remove any inconsistencies or errors that could affect the accuracy of your analysis.
Challenges in Implementation
- One common challenge organizations face when implementing user behavior analytics is ensuring data privacy and security compliance, especially with regulations like GDPR.
- Another challenge is integrating data from multiple sources and systems, which can be complex and time-consuming.
- Organizations also struggle with the interpretation of user behavior data and translating it into actionable insights for decision-making.
Best Practices for Successful Implementation, User Behavior Analytics
- Involve key stakeholders from different departments in the planning and implementation process to ensure alignment with business objectives.
- Define clear metrics and KPIs to measure the success of your user behavior analytics system and track progress towards your goals.
- Regularly communicate findings and insights from the analytics system to relevant teams to drive informed decision-making across the organization.
- Continuously monitor and optimize your user behavior analytics system to adapt to changing business needs and technological advancements.
Benefits of User Behavior Analytics
User Behavior Analytics (UBA) offers numerous advantages when it comes to enhancing cybersecurity measures, improving incident response, and ensuring compliance and risk management. By analyzing user behavior patterns, organizations can proactively detect potential threats and suspicious activities, ultimately strengthening their overall security posture.
Enhancing Cybersecurity
User Behavior Analytics plays a crucial role in enhancing cybersecurity by providing insights into user activities and identifying deviations from normal behavior. This allows organizations to detect insider threats, unauthorized access attempts, and other suspicious activities that may go unnoticed with traditional security measures.
- UBA helps in detecting abnormal user behaviors that indicate potential security incidents.
- It enables organizations to prioritize and respond to security threats more effectively.
- By analyzing user behavior, organizations can strengthen their overall security posture and reduce the risk of data breaches.
Improving Incident Response and Threat Detection
User Behavior Analytics can significantly improve incident response and threat detection capabilities by providing real-time insights into user activities and anomalies. This enables security teams to quickly identify and mitigate security incidents before they escalate, minimizing the impact on the organization.
- UBA helps in identifying advanced persistent threats (APTs) and insider threats in real-time.
- It provides contextual information that enhances the accuracy of threat detection and incident response.
- By correlating user behavior data with other security information, UBA enables comprehensive threat intelligence and analysis.
Role in Compliance and Risk Management
User Behavior Analytics plays a crucial role in compliance and risk management by helping organizations meet regulatory requirements and mitigate potential risks associated with data breaches and security incidents. By continuously monitoring user behavior, organizations can ensure compliance with data protection laws and industry regulations.
UBA assists organizations in identifying and addressing compliance gaps through continuous monitoring of user activities and access controls.
| Examples of Real-World Scenarios: | User Behavior Analytics has been instrumental in: |
|---|---|
| 1. | Detecting insider threats and unauthorized access attempts in financial institutions. |
| 2. | Preventing data exfiltration by identifying anomalous user behaviors in healthcare organizations. |
| 3. | Enhancing incident response capabilities by correlating user behavior data with threat intelligence feeds in technology companies. |
