Understanding Customer Segmentation is like decoding the secret language of your customers, allowing businesses to tailor their strategies with laser precision. Get ready to dive into the world of marketing magic!
Customer segmentation is the key to unlocking valuable insights about your target audience, paving the way for personalized marketing strategies that drive engagement and satisfaction.
Introduction to Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation is the process of dividing a company’s customer base into distinct groups based on specific characteristics. This allows businesses to better understand their target audience, tailor their marketing strategies, and provide more personalized experiences to customers. By analyzing data such as demographics, behavior, and preferences, companies can create targeted campaigns that are more likely to resonate with different segments of their customer base.
Importance of Customer Segmentation, Understanding Customer Segmentation
- Helps companies identify and prioritize high-value customer segments
- Allows for more personalized marketing messages and product offerings
- Improves customer retention and loyalty by addressing specific needs and preferences
- Enhances overall marketing efficiency and ROI by focusing resources on the most profitable segments
Examples of Customer Segmentation in Action
- A clothing retailer may use customer segmentation to target different age groups with specific styles and promotions
- An online streaming service may segment customers based on viewing habits to recommend personalized content
- An airline may offer different loyalty programs based on frequency of travel and spending habits
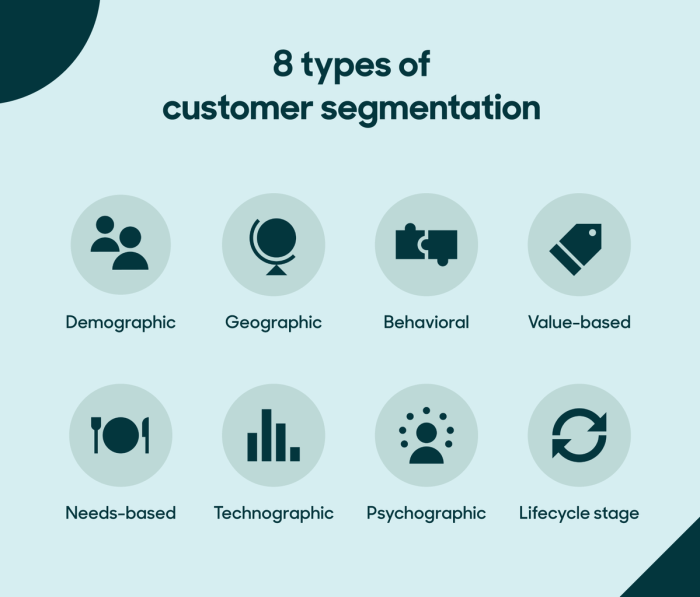
Types of Customer Segmentation: Understanding Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation is crucial in marketing to effectively target specific customer groups. There are different types of customer segmentation, each focusing on different aspects of consumer behavior. Let’s explore the main types:
1. Demographic Segmentation
Demographic segmentation involves dividing customers based on demographic factors such as age, gender, income, education, occupation, etc. For example, a company selling luxury watches may target customers in the age group of 30-50 with high income levels.
2. Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation considers customers’ lifestyle, personality, values, interests, and attitudes. A company selling outdoor gear may target adventure enthusiasts who value experiences and outdoor activities.
3. Behavioral Segmentation
Behavioral segmentation focuses on customers’ purchasing behavior, usage patterns, brand loyalty, and benefits sought. For instance, a coffee chain may offer loyalty rewards to frequent customers to encourage repeat purchases.
4. Geographic Segmentation
Geographic segmentation divides customers based on their location, such as country, region, city, or climate. A company selling winter clothing will target customers in colder regions where the demand for such products is higher.
Each type of segmentation has its own strengths and weaknesses in targeting specific customer groups. Demographic segmentation provides a broad overview of customers but may overlook individual preferences. Psychographic segmentation delves deeper into customer motivations but can be harder to quantify. Behavioral segmentation focuses on actual customer behavior but may not capture changes in preferences over time. Geographic segmentation allows for targeted marketing based on location but may miss out on other important factors influencing consumer behavior.
In conclusion, a combination of these segmentation types can help businesses create more personalized marketing strategies and better connect with their target audience.
Benefits of Understanding Customer Segmentation
Understanding customer segmentation can provide numerous advantages for businesses. By tailoring marketing strategies to specific customer segments, companies can enhance their overall customer experience, leading to increased engagement and loyalty.
Personalized Marketing Campaigns
- Personalized marketing campaigns can be created based on the unique preferences and behaviors of different customer segments.
- By delivering relevant content and offers to specific groups, businesses can increase customer engagement and drive conversions.
- Customers are more likely to respond positively to personalized messages, leading to higher levels of brand loyalty.
Improved Product Development
- Customer segmentation allows businesses to gain insights into the needs and preferences of different customer groups.
- By understanding what each segment values most, companies can develop products that better meet customer expectations.
- Feedback from segmented customers can help identify areas for product improvement, leading to higher levels of customer satisfaction.
Strategies for Effective Customer Segmentation

Effective customer segmentation is crucial for businesses to tailor their marketing strategies and improve customer satisfaction. By implementing best practices and utilizing data analysis, companies can identify distinct customer segments and target them with personalized approaches. Let’s explore some strategies for effective customer segmentation:
The Role of Data Analysis in Identifying Customer Segments
Data analysis plays a critical role in identifying customer segments by examining customer behavior, preferences, and demographics. By analyzing data from various sources such as CRM systems, social media, and website analytics, businesses can uncover patterns and trends that reveal different customer segments. For example, a retail company may use purchase history data to identify high-value customers who prefer luxury products, allowing them to create targeted marketing campaigns for this segment.
Examples of Successful Marketing Strategies Driven by Customer Segmentation
1. Personalized Email Campaigns: By segmenting customers based on their purchase history or browsing behavior, businesses can send personalized email campaigns with product recommendations or exclusive offers tailored to each segment’s preferences. This approach can lead to higher open rates and conversions compared to generic email blasts.
2. Loyalty Programs: Customer segmentation can help businesses identify loyal customers who are likely to engage with a loyalty program. By offering rewards and incentives targeted at specific customer segments, companies can increase customer retention and brand loyalty. For example, airlines often segment customers based on their travel frequency and offer tiered loyalty programs with exclusive benefits for frequent flyers.
3. Geographic Targeting: Businesses can use customer segmentation to target specific geographic regions with localized marketing campaigns. By understanding the unique preferences and needs of customers in different locations, companies can tailor their messaging and promotions to resonate with each segment. For instance, a fast-food chain may offer region-specific promotions or menu items based on customer preferences in each location.
Incorporating these strategies can help businesses effectively segment their customers and create targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with each segment’s preferences and behaviors.
