Diving deep into Interest rates and mortgages, get ready to explore the intricate web of financial jargon and economic influences that shape our borrowing decisions. From the ebb and flow of interest rates to the different types of mortgages available, this journey promises to unravel the mysteries behind your monthly payments.
As we navigate through the realms of fixed-rate and adjustable-rate mortgages, brace yourself for a rollercoaster of insights that will leave you enlightened and empowered in the realm of home financing.
Overview of Interest Rates
Interest rates play a crucial role in determining the cost of borrowing money, especially when it comes to mortgages. When interest rates are low, borrowers can take out loans at a lower cost, resulting in lower monthly mortgage payments. On the other hand, when interest rates are high, borrowing becomes more expensive, leading to higher monthly payments for mortgages.
Impact of Fluctuating Interest Rates
Fluctuating interest rates can have a significant impact on the overall cost of borrowing for a mortgage. For example, consider a scenario where a borrower takes out a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage of $200,000. If the interest rate is 3%, the monthly payment would be approximately $843. If the interest rate increases to 4%, the monthly payment would jump to around $955. Over the life of the loan, this 1% increase in interest rate would result in thousands of dollars in additional interest payments.
Role of Central Banks
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States, play a crucial role in setting short-term interest rates. By adjusting the federal funds rate, central banks can influence borrowing costs for consumers and businesses. When central banks lower interest rates, borrowing becomes cheaper, stimulating economic activity. Conversely, when central banks raise interest rates, borrowing becomes more expensive, which can help to control inflation.
Types of Mortgages
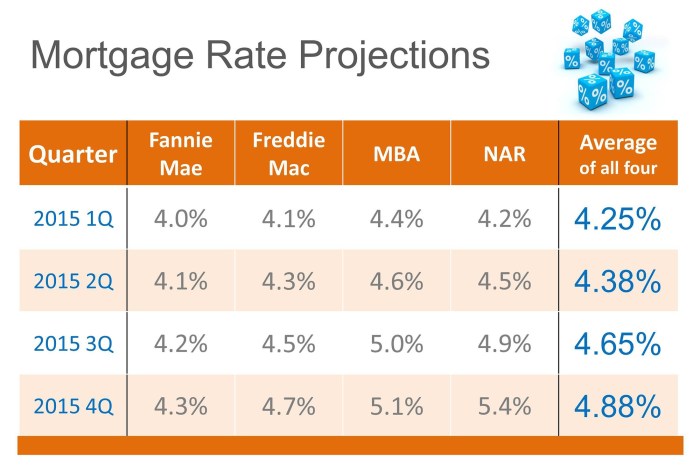
When it comes to mortgages, there are two main types that borrowers can choose from – fixed-rate mortgages and adjustable-rate mortgages. Each type has its own set of advantages and considerations that borrowers should be aware of before making a decision.
Fixed-Rate Mortgages vs. Adjustable-Rate Mortgages
Fixed-rate mortgages have a stable interest rate that does not change over the life of the loan. This provides borrowers with predictability and stability in their monthly payments, making it easier to budget and plan for the long term. On the other hand, adjustable-rate mortgages have interest rates that can fluctuate based on market conditions. While initial rates may be lower than fixed-rate mortgages, there is a risk of rates increasing in the future, potentially leading to higher monthly payments.
How Fixed-Rate Mortgages Provide Stability in Payments
With a fixed-rate mortgage, borrowers know exactly how much they need to pay each month for the entire duration of the loan. This stability can be reassuring for borrowers who prefer predictable payments and want to avoid any surprises or fluctuations in their monthly expenses.
How Adjustable-Rate Mortgages Can Benefit Borrowers
Adjustable-rate mortgages can benefit borrowers who plan to sell or refinance their home within a few years. Initially, these mortgages often come with lower interest rates compared to fixed-rate mortgages, which can result in lower monthly payments during the introductory period. This flexibility may be advantageous for borrowers who expect changes in their financial situation or housing needs in the near future.
Factors Influencing Interest Rates
Interest rates are influenced by a variety of factors that can impact borrowing costs for consumers. Let’s explore some of the key economic indicators that affect interest rate trends, how inflation rates impact mortgage interest rates, and the relationship between bond yields and mortgage rates.
Economic Indicators
- The Federal Reserve: The Federal Reserve plays a crucial role in setting the federal funds rate, which in turn influences short-term interest rates. Changes in the federal funds rate can have a ripple effect on other interest rates, including those for mortgages.
- Economic Growth: Strong economic growth typically leads to higher interest rates as demand for loans increases. Conversely, a sluggish economy may result in lower interest rates to stimulate borrowing and spending.
- Unemployment Rate: The unemployment rate can impact interest rates, with lower unemployment often correlating with higher interest rates due to increased consumer spending and borrowing.
Inflation Rates and Mortgage Interest Rates
- Inflation refers to the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising. Mortgage lenders factor inflation expectations into interest rates to ensure they earn a real return on their loans.
- When inflation is high, lenders may increase interest rates to protect the purchasing power of the money they will receive in the future. On the other hand, low inflation may lead to lower interest rates to attract borrowers.
- Homebuyers should keep an eye on inflation trends as they can directly impact mortgage rates, making it important to consider inflation when deciding on the timing of a home purchase.
Bond Yields and Mortgage Rates
- Bond yields and mortgage rates are closely related, as both are influenced by similar economic factors such as inflation expectations, economic growth, and the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy.
- Generally, when bond yields rise, mortgage rates tend to follow suit. This is because higher bond yields make borrowing more expensive for lenders, leading them to charge higher interest rates on mortgages.
- Conversely, when bond yields fall, mortgage rates may decrease as lenders can borrow money at lower rates, allowing them to offer more competitive terms to homebuyers.
Mortgage Rates Forecasting
When it comes to forecasting mortgage rates, experts analyze a variety of factors to predict potential changes. These factors include economic indicators, inflation rates, bond yields, and Federal Reserve policies. By closely monitoring these indicators, analysts can make educated predictions about the direction of mortgage rates in the future.
Geopolitical Events Impact
Geopolitical events such as wars, trade disputes, and political instability can have a significant impact on mortgage rates. Uncertainty in the global political landscape can lead to market volatility, causing investors to seek safer assets like bonds. This increased demand for bonds can drive interest rates lower, including mortgage rates. Conversely, positive geopolitical developments can lead to higher rates as investors become more willing to take on riskier assets.
Economic Data Releases Significance
Economic data releases, such as employment reports, GDP growth figures, and consumer spending data, play a crucial role in interest rate predictions. Strong economic data often leads to expectations of higher inflation, prompting the Federal Reserve to raise interest rates to curb inflation. This, in turn, can push mortgage rates higher. On the other hand, weak economic data may signal a slowing economy, prompting the Fed to lower rates to stimulate growth, potentially leading to lower mortgage rates.
